31 Jan Case Hardening Steels
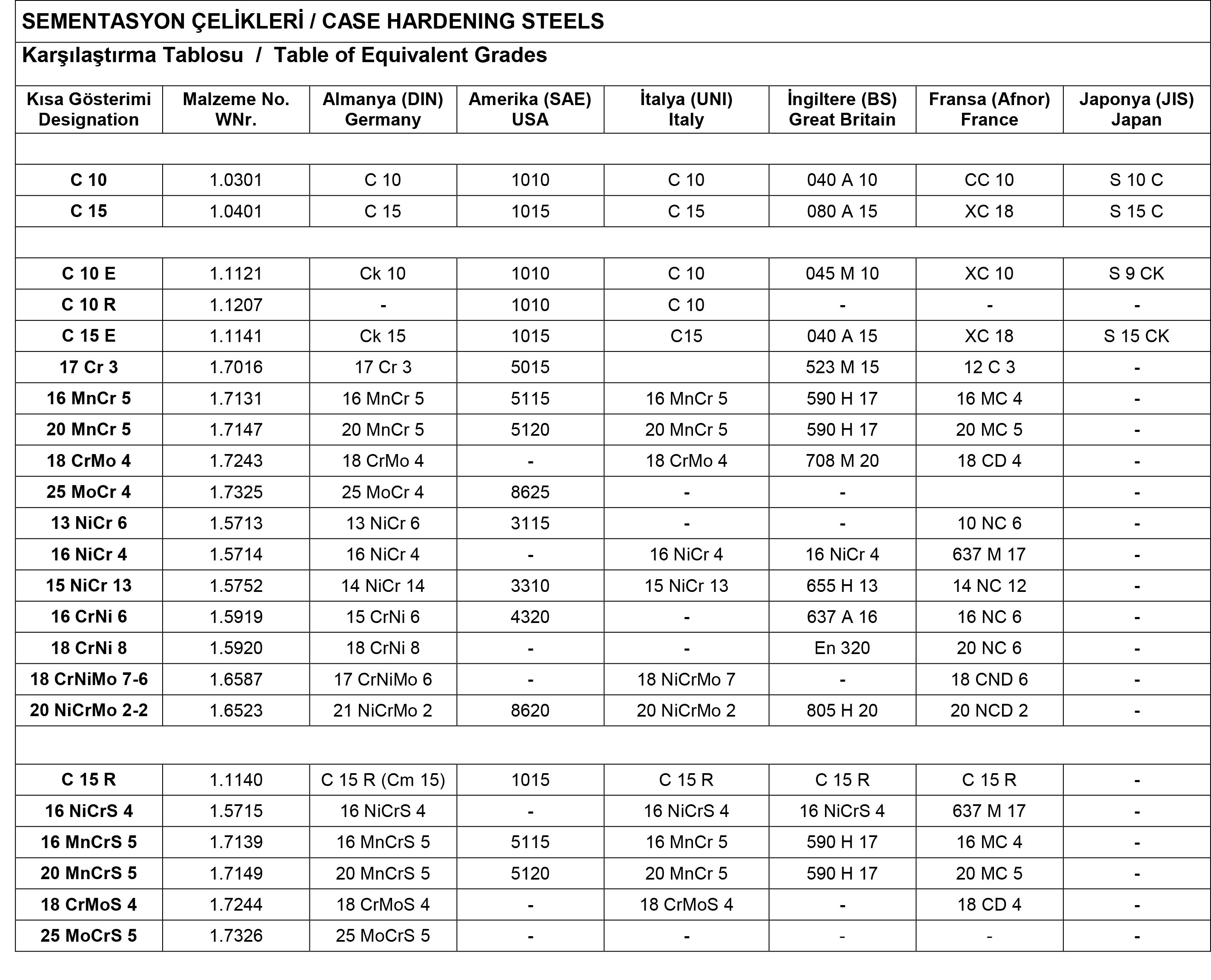
Case Hardening Steel is an alloyed or non alloyed low carbon steel with high resistant against wearing on the surface, tough and soft at core, which is used in production of parts resistant against wearing and impact stresses. To obtain the mentoned properties of the material is achieved by carburizing of the surface which is called cementation. Carburization is the enrichening with carbon in an area limited to the edges by holding the temperature above transformation points Ac1, or Ac3 in carbon releasing media. There are several method of cementation as shown below ;
- Solid Media Cementation
- Cementation in Salt Bath
- Gas Cementation
To reach the required cementation depth and hardness, microcleanness of the material and grain size have to be suitable while cementation time and temperature have to be taken under control at the same time. The carburization depth is determined by the time required for cementation and the activity of the carburization media. Generally, case hardening temperatures lie at about 8700-9300C but sometimes higher temperatures are used. Cementation results as different hardness values due to the cementation method and the hardening method used after cementation. Hardened steels are used in the production of gears, shafts, piston pins, chain links, chain gears and pulleys, disks, bearing pedestral, rollers, certain masurement and control devices, medium stress and stress parts, cold headed or jetting (extrusion) parts, cutting tools.
ADVANTAGES OF CASE HARDENING STEELS
- Hard, wear resistant surface
- Tough ductile core
- Increased strenght
- Possible substitute for through hardening steels
- Surface and core hardness can be closely controlled
- Wide selection of metals
- Close dimensional tolerances by grinding and honing
- Excellent stability at low temperatures
- Generation of localized hard, soft and tough areas possible
- Wide range of mechanical design